Big O: Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency
Big O(oh) is an essential tool for computer scientists to analyze the complexity and cost of an algorithm,
and an important practice for software engineers to understand algorithms more deeply.
Good Code:
- Readability
- Scalable (Big O)
Every computer will take a different time to run this code there are a lot of factors to consider like CPU, what I’m running on my pc, what other programming languages are using etc.
So how to know whose have better codes?
Big-O notation talks about how much my code takes time to run
Big-O Complexity Chart

When growing bigger & bigger with our input how much does the func or algorithm slow down
Big O: Analysis of Algorithm Efficiency —
Big-O Cheat Sheet

 —
—
O(n): the most common big=O notation
As the number of the elements increases the # of operations will increase.
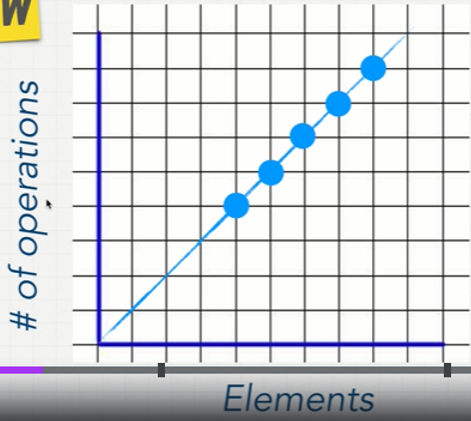
O(n): Constant Time
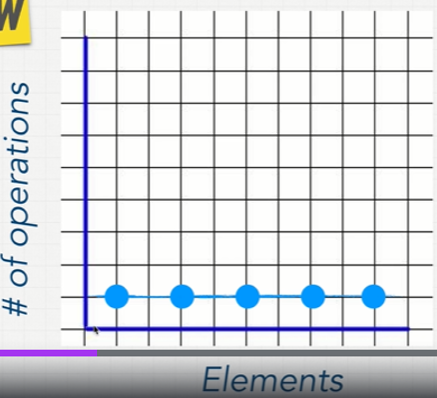
on big-o complexity chart, its performance consider as excellent
For more interesting details about: What is the difference between big oh, big omega and big theta notations?
Exercise01: Big-O Calculation
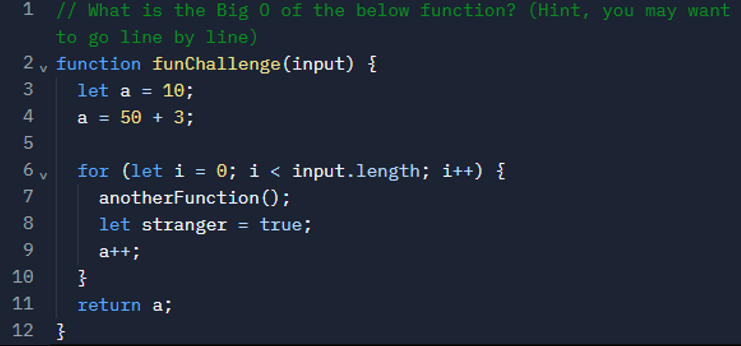
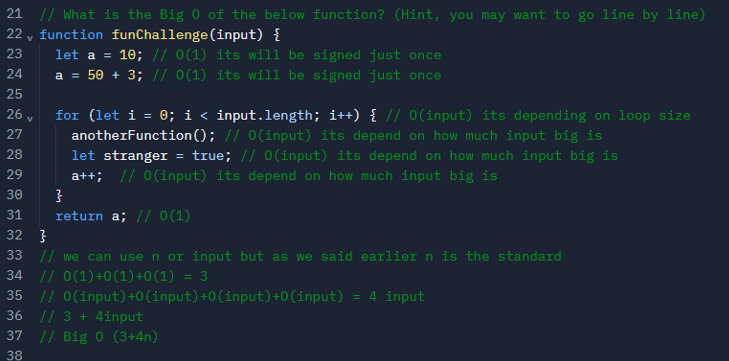
Exercise02: Big-O Calculation
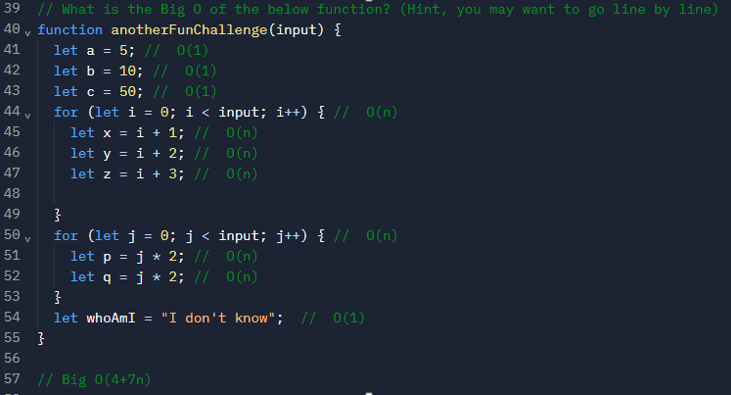
In interviews, we don’t calculate things like that, we have 4 rules to know the big O notation like a ninja:
- Worst case
- Remove constant
- Different terms for inputs
- Drop non-dominate
Review
Big O: The worst case analysis of algorithm efficiency.Running Time: The amount of time required for an algorithm to complete.Memory Space: The amount of memory resources required for an algorithm to complete.Input Size: Represented by the variable n, the total size of values used as parameters in an algorithm.Big Omega: The best case analysis of algorithm efficiency.Big Theta: The typical or random case used for analysis of algorithm efficiency.
Linked Lists
What is a Linked List
A Linked List is a sequence of Nodes that are connected/linked to each other. The most defining feature of a Linked List is that each Node references the next Node in the link.
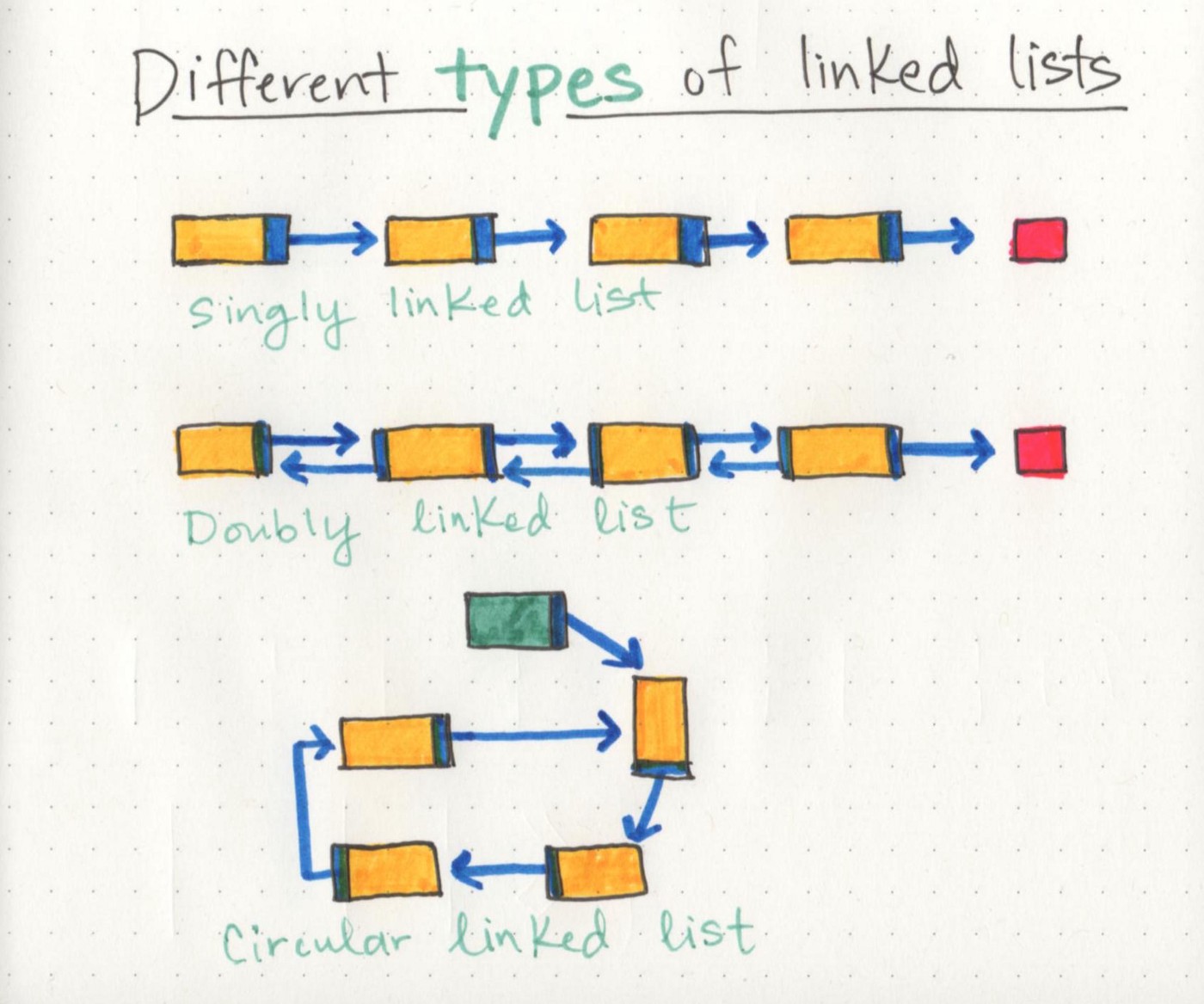
There are two types of Linked List - Singly and Doubly. We will be implementing a Singly Linked List in this implementation.
Terminology
- Linked List - A data structure that contains nodes that links/points to the next node in the list.
- Singly - Singly refers to the number of references the node has. A Singly linked list means that there is only one reference, and the reference points to the Next node in a linked list.
- Doubly - Doubly refers to there being two (double) references within the node. A Doubly linked list means that there is a reference to both the Next and Previous node.
- Node - Nodes are the individual items/links that live in a linked list. Each node contains the data for each link.
- Next - Each node contains a property called Next. This property contains the reference to the next node.
- Head - The Head is a reference of type Node to the first node in a linked list.
- Current - The Current is a reference of type Node to the node that is currently being looked at. When traversing, you create a new Current variable at the Head to guarantee you are starting from the beginning of the linked list.
For more interesting details about:
- What is a Linked List
- Terminology:
- What does it look like
- Traversal
- Adding a Node
- Print Out Nodes
- Prerequisites
A node only knows about what data it contains, and who its neighbor is.
Different types of linked lists
a linked list is usually efficient when it comes to adding and removing most elements, but can be very slow to search and find a single element.